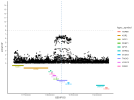
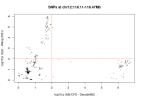
CHROMOSOME 12 (GWAS-2)
Chr12 contained three Tier 1 genes.
Image of the 2025 DecodeME results by @ME/CFS Science Blog:

********************
SUDS3 (Tier 1)
• Protein: SIN3A corepressor complex component, also known as SDS3. UniProt. GeneCards.
The allele that increases the risk of ME/CFS is associated with increased SUDS3 expression.7
• Molecular function: Regulatory protein that represses transcription and augments histone deacetylase activity of HDAC1 (UniProt). SUDS3 alters expression of the upstream kinase, ASK1, in the p38 MAPK pathway cascade (44).
• Cellular function: Chromatin remodeling and transcriptional regulation. Depletion of mouse Suds3 reveals an essential role in early lineage specification (45).
• Link to disease: Proposed to contribute to the microglial inflammatory response (44).
• Potential relevance to ME/CFS: Unclear, but potentially to neuroinflammation.
*******************
References
7. Johnson BS, Farkas D, El-Mergawy R, Adair JA, Elhance A, Eltobgy M, et al. Targeted degradation of extracellular mitochondrial aspartyl-tRNA synthetase modulates immune responses. Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 1;15(1).
44. Shen J, Lai W, Li Z, Zhu W, Bai X, Yang Z, et al. SDS3 regulates microglial inflammation by modulating the expression of the upstream kinase ASK1 in the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. 2024 Sep;73(9):1547–64.
(note SDS3 is an earlier name for SUDS3)
45. Zhang K, Dai X, Wallingford MC, Mager J. Depletion of Suds3 reveals an essential role in early lineage specification. Dev Biol. 2013 Jan 15;373(2):359–72.
Chr12 contained three Tier 1 genes.
Image of the 2025 DecodeME results by @ME/CFS Science Blog:
********************
SUDS3 (Tier 1)
• Protein: SIN3A corepressor complex component, also known as SDS3. UniProt. GeneCards.
The allele that increases the risk of ME/CFS is associated with increased SUDS3 expression.7
• Molecular function: Regulatory protein that represses transcription and augments histone deacetylase activity of HDAC1 (UniProt). SUDS3 alters expression of the upstream kinase, ASK1, in the p38 MAPK pathway cascade (44).
• Cellular function: Chromatin remodeling and transcriptional regulation. Depletion of mouse Suds3 reveals an essential role in early lineage specification (45).
• Link to disease: Proposed to contribute to the microglial inflammatory response (44).
• Potential relevance to ME/CFS: Unclear, but potentially to neuroinflammation.
*******************
References
7. Johnson BS, Farkas D, El-Mergawy R, Adair JA, Elhance A, Eltobgy M, et al. Targeted degradation of extracellular mitochondrial aspartyl-tRNA synthetase modulates immune responses. Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 1;15(1).
44. Shen J, Lai W, Li Z, Zhu W, Bai X, Yang Z, et al. SDS3 regulates microglial inflammation by modulating the expression of the upstream kinase ASK1 in the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. 2024 Sep;73(9):1547–64.
(note SDS3 is an earlier name for SUDS3)
45. Zhang K, Dai X, Wallingford MC, Mager J. Depletion of Suds3 reveals an essential role in early lineage specification. Dev Biol. 2013 Jan 15;373(2):359–72.
Last edited: