Systemic increase of AMPA receptors associated with cognitive impairment of long COVID
Long COVID primarily presents with persistent cognitive impairment (Cog-LC), imposing a substantial and lasting global burden. Even after the pandemic, there remains a critical global need for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies targeting Cog-LC. Nevertheless, the underlying neural mechanisms remain poorly understood. Given the central role of synapses in brain function, investigation of synaptic molecular changes may provide vital insights into Cog-LC pathophysiology.
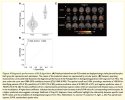
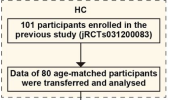
In this study, we used [11C]K-2 PET to characterize the density of AMPA receptors (AMPARs) on the post-synaptic cell surface, which are crucial synaptic components in brain signalling. Statistical parametrical mapping was used to spatially normalize and apply independent t-test for a voxel-based comparison. We selected patients with Cog-LC (n = 30) based on Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status assessed persistent cognitive impairment and healthy controls (n = 80) with no diagnosed neuropsychiatric disorders. The primary objective was to compare [11C]K-2 standardized uptake value ratio with white matter (SUVRWM) as a reference region between patients with Cog-LC and healthy controls, and to define the regional extent of differences. The secondary objective was to examine associations between [11C]K-2 SUVRWM and plasma concentrations of cytokines or chemokines. As an exploratory objective, we tested whether [11C]K-2 PET data could distinguish Cog-LC from healthy controls using a partial least squares based classification algorithm.
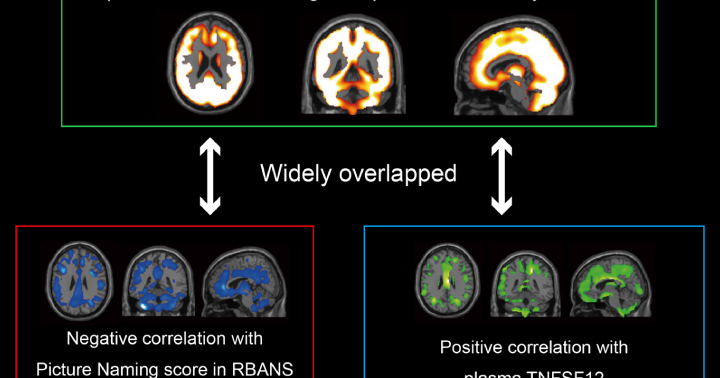
A voxel-based comparison (P < 0.05, T > 1.66, one-tailed, false discovery rate control) and a volume of interests analysis (P < 0.05, Bonferroni multiple comparison) demonstrated that increased index of AMPAR density in large parts of the brains of patients with Cog-LC compared with that in healthy controls. A voxel-based correlation analysis also showed the brain regions where [11C]K-2 SUVRWM correlated positively with plasma TNFSF12 and negatively with plasma CCL2 concentrations. A partial least squares model trained on the index of AMPAR density data demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy, achieving 100% sensitivity and 91.2% specificity. [11C]K-2 PET signal represents the index of AMPAR density on the post-synaptic neural cell surface, not on the glial cell surface.
A systemic increase in synaptic AMPARs across the brain may drive abnormal information processing in Cog-LC and, through excessive excitatory signalling, pose a risk of excitotoxic neuronal damage. We derived the hypothesis that [11C]K-2 PET would be helpful in establishing a diagnostic framework for Cog-LC and that antagonists for cell surface AMPARs, such as perampanel, would be a potential therapeutic target. These hypotheses should be investigated in future large-scale clinical studies.
Web | PDF | Brain Communications | Open Access
Fujimoto, Yu; Abe, Hiroki; Eiro, Tsuyoshi; Tsugawa, Sakiko; Tanaka, Meiro; Hatano, Mai; Nakajima, Waki; Ichijo, Sadamitsu; Arisawa, Tetsu; Takada, Yuuki; Kimura, Kimito; Sano, Akane; Hirahata, Koichi; Sasaki, Nobuyuki; Kimura, Yuichi; Takahashi, Takuya
Long COVID primarily presents with persistent cognitive impairment (Cog-LC), imposing a substantial and lasting global burden. Even after the pandemic, there remains a critical global need for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies targeting Cog-LC. Nevertheless, the underlying neural mechanisms remain poorly understood. Given the central role of synapses in brain function, investigation of synaptic molecular changes may provide vital insights into Cog-LC pathophysiology.
In this study, we used [11C]K-2 PET to characterize the density of AMPA receptors (AMPARs) on the post-synaptic cell surface, which are crucial synaptic components in brain signalling. Statistical parametrical mapping was used to spatially normalize and apply independent t-test for a voxel-based comparison. We selected patients with Cog-LC (n = 30) based on Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status assessed persistent cognitive impairment and healthy controls (n = 80) with no diagnosed neuropsychiatric disorders. The primary objective was to compare [11C]K-2 standardized uptake value ratio with white matter (SUVRWM) as a reference region between patients with Cog-LC and healthy controls, and to define the regional extent of differences. The secondary objective was to examine associations between [11C]K-2 SUVRWM and plasma concentrations of cytokines or chemokines. As an exploratory objective, we tested whether [11C]K-2 PET data could distinguish Cog-LC from healthy controls using a partial least squares based classification algorithm.
A voxel-based comparison (P < 0.05, T > 1.66, one-tailed, false discovery rate control) and a volume of interests analysis (P < 0.05, Bonferroni multiple comparison) demonstrated that increased index of AMPAR density in large parts of the brains of patients with Cog-LC compared with that in healthy controls. A voxel-based correlation analysis also showed the brain regions where [11C]K-2 SUVRWM correlated positively with plasma TNFSF12 and negatively with plasma CCL2 concentrations. A partial least squares model trained on the index of AMPAR density data demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy, achieving 100% sensitivity and 91.2% specificity. [11C]K-2 PET signal represents the index of AMPAR density on the post-synaptic neural cell surface, not on the glial cell surface.
A systemic increase in synaptic AMPARs across the brain may drive abnormal information processing in Cog-LC and, through excessive excitatory signalling, pose a risk of excitotoxic neuronal damage. We derived the hypothesis that [11C]K-2 PET would be helpful in establishing a diagnostic framework for Cog-LC and that antagonists for cell surface AMPARs, such as perampanel, would be a potential therapeutic target. These hypotheses should be investigated in future large-scale clinical studies.
Web | PDF | Brain Communications | Open Access