LarsSG
Senior Member (Voting Rights)
Published as a preprint. See post #7
And now published in final form - link here
******
This is an abstract from the Demystifying Long COVID International Conference 2023, converted from an image on Twitter, so it might be slightly wonky, but it looks intriguing.
Blood Transcriptomics Reveal Persistent SARS-COV-2 RNA And Candidate Clinical Biomarkers in A Belgian Long COVID Cohort
Menezes S, Jamoulle M, Carletto M, Van Holm B, Moens L, Meyts I, Maes P, Van Weyenbergh
Background: With millions of people currently suffering from Long COVID (LC), validated therapeutic options and biomarkers are direly needed to guide clinical management. In this study, we propose whole blood transcriptomics to identify non-invasive candidate biomarkers for viral persistence, disease severity and clinical evolution in a general practice-based cohort.
Materials and Methods: A cohort of LC patients (diagnosis according to WHO criteria) was followed up for 1-30 months after acute COVID. Complete clinical history and follow-up was obtained at a single general practice (MJ, Charleroi, Belgium) using electronic health records and several established clinical scales (DUSOI Duke Severity Overall Index, COOP Dartmouth Coop chart initiative) were used to quantify patient evolution. Severe neurocognitive deficits were confirmed by brain scintigraphy (SPECT), with 25/48 patients (52%) displaying vascular defects.
Whole blood samples were obtained from 48 LC patients and 12 controls (matched for age, sex, time since acute COVID-19, vaccination status and comorbidities) and analyzed by digital transcriptomic analysis (nCounter, Nanostring) to quantify a total of 800 RNAS (SARSCOV2 and innate/adaptive immunity), as previously established for critical COVID-19 (Menezes et al., Lancet Microbe 2021). Neutralizing antibodies against 10 different SARSCOV2 variants. were quantified using a sensitive electrochemoluminescent assay (MSD). Statistical analysis included non-parametric Mann- Whitney test, Spearman correlation and multivariable logistic regression.
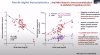
Results: Digital transcriptomic analysis revealed a total of 212 differentially expressed genes between LC patients and matched controls.
Among 120 transcripts significantly increased in LC were several viral RNAs: Nucleocapsid, ORF7A, ORF3A, Mpro (target of Paxlovid) and antisense RNA, the latter suggesting ongoing viral replication, while Spike RNA was remarkably low/absent. In addition, several SARSCOV2-realted host genes were also increased in LC (ACE2/TMPRSS2 receptors and DPP4/FURIN proteases). Other upregulated RNAs were specific for memory B cells (CD27/IGHE/BMP8A), and platelets (CD99/PBX1/PDZK1IP1). Platelet transcripts were also positively corelated to viral load (p<10-7), providing a mechanistic link to the hypercoagulative state previously demonstrated in LC. Summarizing these 800 transcripts into biological pathways, we found significantly decreased TLR signaling (p=0.0039), lymphocyte activation (p=0.016) and immunometabolism (p=0.023) in LC patients. Moreover, immunometabolism was negatively correlated with blood viral load (R=-0.56, p<0.0001), suggesting an "exhausted" immune status in LC due to ongoing viral replication.
Using multivariable regression, we found that age and sex were not associated with "low" vs. "high" viral RNA status, whereas the number of comorbidities (1.61 95% CI [1.14-2.49], p=0.014) and the number of COVID vaccine doses (0.36 95% were CI [0.14-0.79], p=0.018) independent predictors of "low" vs. "high" status, confirming a protective role of vaccination. SPECT-positive patients could be discriminated from SPECT- negative by increased RNA levels of insulin receptor (INSR) and platelet P-selectin (SELP), further incriminating perturbated platelet
and (immuno)metabolism activation/coagulation in disease severity.
Conclusions: We used digital transcriptomics to identify non-invasive (blood) biomarkers for viral persistence, disease severity and clinical evolution, guided by SPECT imaging. Overall, increased platelet RNAs and decreased immunometabolism are significantly correlated to viral load, providing mechanistic links as well as therapeutic targets to tackle Long COVID.
Demystifying Long COVID International Conference 2023
And now published in final form - link here
******
This is an abstract from the Demystifying Long COVID International Conference 2023, converted from an image on Twitter, so it might be slightly wonky, but it looks intriguing.
Blood Transcriptomics Reveal Persistent SARS-COV-2 RNA And Candidate Clinical Biomarkers in A Belgian Long COVID Cohort
Menezes S, Jamoulle M, Carletto M, Van Holm B, Moens L, Meyts I, Maes P, Van Weyenbergh
Background: With millions of people currently suffering from Long COVID (LC), validated therapeutic options and biomarkers are direly needed to guide clinical management. In this study, we propose whole blood transcriptomics to identify non-invasive candidate biomarkers for viral persistence, disease severity and clinical evolution in a general practice-based cohort.
Materials and Methods: A cohort of LC patients (diagnosis according to WHO criteria) was followed up for 1-30 months after acute COVID. Complete clinical history and follow-up was obtained at a single general practice (MJ, Charleroi, Belgium) using electronic health records and several established clinical scales (DUSOI Duke Severity Overall Index, COOP Dartmouth Coop chart initiative) were used to quantify patient evolution. Severe neurocognitive deficits were confirmed by brain scintigraphy (SPECT), with 25/48 patients (52%) displaying vascular defects.
Whole blood samples were obtained from 48 LC patients and 12 controls (matched for age, sex, time since acute COVID-19, vaccination status and comorbidities) and analyzed by digital transcriptomic analysis (nCounter, Nanostring) to quantify a total of 800 RNAS (SARSCOV2 and innate/adaptive immunity), as previously established for critical COVID-19 (Menezes et al., Lancet Microbe 2021). Neutralizing antibodies against 10 different SARSCOV2 variants. were quantified using a sensitive electrochemoluminescent assay (MSD). Statistical analysis included non-parametric Mann- Whitney test, Spearman correlation and multivariable logistic regression.
Results: Digital transcriptomic analysis revealed a total of 212 differentially expressed genes between LC patients and matched controls.
Among 120 transcripts significantly increased in LC were several viral RNAs: Nucleocapsid, ORF7A, ORF3A, Mpro (target of Paxlovid) and antisense RNA, the latter suggesting ongoing viral replication, while Spike RNA was remarkably low/absent. In addition, several SARSCOV2-realted host genes were also increased in LC (ACE2/TMPRSS2 receptors and DPP4/FURIN proteases). Other upregulated RNAs were specific for memory B cells (CD27/IGHE/BMP8A), and platelets (CD99/PBX1/PDZK1IP1). Platelet transcripts were also positively corelated to viral load (p<10-7), providing a mechanistic link to the hypercoagulative state previously demonstrated in LC. Summarizing these 800 transcripts into biological pathways, we found significantly decreased TLR signaling (p=0.0039), lymphocyte activation (p=0.016) and immunometabolism (p=0.023) in LC patients. Moreover, immunometabolism was negatively correlated with blood viral load (R=-0.56, p<0.0001), suggesting an "exhausted" immune status in LC due to ongoing viral replication.
Using multivariable regression, we found that age and sex were not associated with "low" vs. "high" viral RNA status, whereas the number of comorbidities (1.61 95% CI [1.14-2.49], p=0.014) and the number of COVID vaccine doses (0.36 95% were CI [0.14-0.79], p=0.018) independent predictors of "low" vs. "high" status, confirming a protective role of vaccination. SPECT-positive patients could be discriminated from SPECT- negative by increased RNA levels of insulin receptor (INSR) and platelet P-selectin (SELP), further incriminating perturbated platelet
and (immuno)metabolism activation/coagulation in disease severity.
Conclusions: We used digital transcriptomics to identify non-invasive (blood) biomarkers for viral persistence, disease severity and clinical evolution, guided by SPECT imaging. Overall, increased platelet RNAs and decreased immunometabolism are significantly correlated to viral load, providing mechanistic links as well as therapeutic targets to tackle Long COVID.
Demystifying Long COVID International Conference 2023
Last edited by a moderator: