Dolphin
Senior Member (Voting Rights)
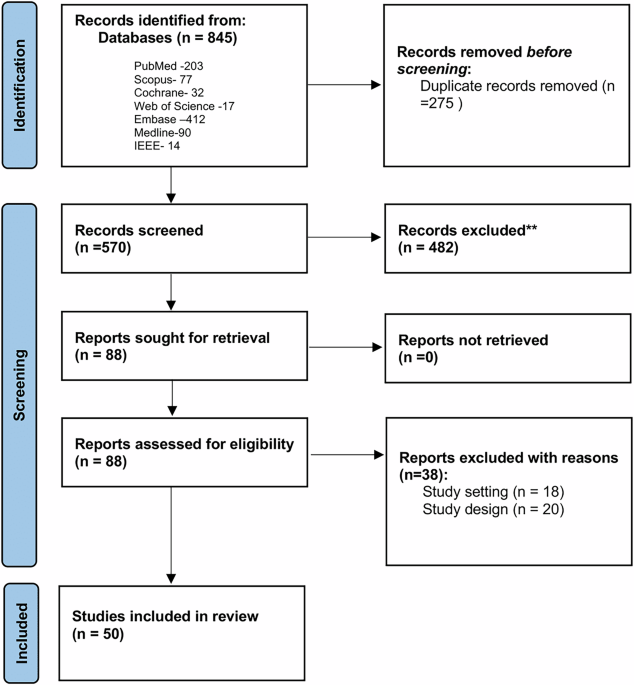
Systematic review: digital biomarkers of fatigue in chronic diseases - npj Digital Medicine
This systematic review explores the relationship between digital biomarkers, measured using wearable devices, and fatigue in patients with chronic diseases. Studies included in this review focused on individuals with diseases or conditions in 13 broad categories: multiple sclerosis (MS)...
- Article
- Open access
- Published: 08 October 2025
Systematic review: digital biomarkers of fatigue in chronic diseases
npj Digital Medicine volume 8, Article number: 602 (2025) Cite this articleAbstract
This systematic review explores the relationship between digital biomarkers, measured using wearable devices, and fatigue in patients with chronic diseases.Studies included in this review focused on individuals with diseases or conditions in 13 broad categories: multiple sclerosis (MS); rheumatoid arthritis (RA); chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); long COVID; cancer; chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS); pulmonary sarcoidosis; Parkinson’s disease; chronic stroke; chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease (CIRD); Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD), Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome (PSS), and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE).
The review synthesizes findings on the correlation between objective digital biomarkers and self-reported fatigue, highlighting the potential for disease-specific digital biomarkers to inform personalized fatigue management.
The results suggest that reduced physical activity, increased sedentary behavior and autonomic dysfunction are associated with fatigue levels across multiple disease conditions included in this review, though the strength of this association and the specific biomarkers involved vary across diseases.
