Risk of post-acute symptoms among adults: A comparison study of severe COVID-19, pneumonia, and influenza
Caroline M. Schaefer, Trudy Millard Krause, George L. Delclos, Raymond S. Greenberg
[Line breaks added]
Background
A retrospective cohort study was undertaken to assess the relationship between initial disease severity of COVID-19 and the risk of post-acute symptoms. The COVID-19 cohort was compared against influenza and pneumonia cohorts to assess whether risk of post-acute symptoms differed.
Methods
Administrative health claims data were obtained for commercially insured and Medicare Advantage covered adults (≥ 18 years) with symptomatic laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 diagnosed in 2020 (n=121,205), and similar cohorts of influenza (n=20,844) and pneumonia (n=29,052) patients diagnosed prior to the pandemic. Post-acute symptoms were assessed at four weeks, three and six months following initial diagnosis.
Results
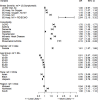
Among the patients with COVID-19, the likelihood of any post-acute symptom increased with initial disease severity, and was also influenced by the presence of comorbidities, especially rheumatoid arthritis, ischemic heart disease and asthma.
The specific post-acute symptoms varied by age, with increased risks of anxiety and headache among the young, whereas the elderly experienced increased brain fog and fatigue.
When compared against the influenza and pneumonia cohorts, all three groups experienced post-acute symptoms, with a strong relationship to disease severity, and only partial resolution over the six-month observation period. Those with influenza were less likely than those with COVID-19 to experience post-acute symptoms while those with pneumonia were more likely to have post-acute illness than those with COVID-19.
Conclusions
Using a large national dataset, we found that COVID-19 symptomology could not be described by previously seen influenza or pneumonia symptomology and differences exist in the prevalence of symptoms as well as time to resolution, better characterizing “long COVID” and identifying that these differences are unique to COVID-19.
Link | PDF (PLOS One) [Open Access]
Caroline M. Schaefer, Trudy Millard Krause, George L. Delclos, Raymond S. Greenberg
[Line breaks added]
Background
A retrospective cohort study was undertaken to assess the relationship between initial disease severity of COVID-19 and the risk of post-acute symptoms. The COVID-19 cohort was compared against influenza and pneumonia cohorts to assess whether risk of post-acute symptoms differed.
Methods
Administrative health claims data were obtained for commercially insured and Medicare Advantage covered adults (≥ 18 years) with symptomatic laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 diagnosed in 2020 (n=121,205), and similar cohorts of influenza (n=20,844) and pneumonia (n=29,052) patients diagnosed prior to the pandemic. Post-acute symptoms were assessed at four weeks, three and six months following initial diagnosis.
Results
Among the patients with COVID-19, the likelihood of any post-acute symptom increased with initial disease severity, and was also influenced by the presence of comorbidities, especially rheumatoid arthritis, ischemic heart disease and asthma.
The specific post-acute symptoms varied by age, with increased risks of anxiety and headache among the young, whereas the elderly experienced increased brain fog and fatigue.
When compared against the influenza and pneumonia cohorts, all three groups experienced post-acute symptoms, with a strong relationship to disease severity, and only partial resolution over the six-month observation period. Those with influenza were less likely than those with COVID-19 to experience post-acute symptoms while those with pneumonia were more likely to have post-acute illness than those with COVID-19.
Conclusions
Using a large national dataset, we found that COVID-19 symptomology could not be described by previously seen influenza or pneumonia symptomology and differences exist in the prevalence of symptoms as well as time to resolution, better characterizing “long COVID” and identifying that these differences are unique to COVID-19.
Link | PDF (PLOS One) [Open Access]