Psychometric evaluation of the PROMIS® physical function short form 12a for use by adults with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome
BACKGROUND
Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a debilitating, long-term illness that significantly impairs physical functioning. Despite its impact, the use of modern generic instruments to assess physical function in this population remains underexplored. This study aims to assess the psychometric properties of the Patient-Reported Outcome Measurement Information System® (PROMIS) Physical Function Short Form (PF-SF) 12a for use in adults with ME/CFS.
METHODS
This study included 334 participants (173 with ME/CFS and 161 healthy controls) who took part in a Cognitive and Exercise sub-study of the Multi-Site Clinical Assessment of ME/CFS study from six clinics across the US. Data was used to examine the ceiling/floor effects, internal consistency reliability, known-groups validity, and convergent validity of the PROMIS PF-SF.
RESULTS
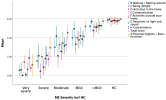
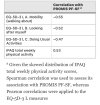
The mean T-score of the PROMIS PF-SF was 40.5 for participants with ME/CFS, about one standard deviation below the national norm (T-score = 50). The PROMIS PF-SF showed no substantial floor/ceiling effects and high internal consistency (standardized Cronbach’s α = 0.88 and ω = 0.92). In addition, this instrument showed good known-groups validity with medium-to-large effect sizes (η2 = 0.08–0.35). A significant, monotonic increase of the physical function score was found across ME/CFS participant groups with low, medium, and high functional impairment as defined by four different measures. Participants with ME/CFS had significantly worse physical function scores than healthy controls (η2 = 0.70). The PROMIS PF-SF also demonstrated good convergent validity with high correlations (magnitude of r = 0.47–0.55) with other relevant measures.
CONCLUSIONS
The PROMIS PF-SF 12a demonstrated satisfactory reliability and validity for use in ME/CFS research and clinical practice.
Web | PDF | Health and Quality of Life Outcomes | Open Access
Yang, Manshu; Keller, San; Rafiee, Parisa; Lin, Jin-Mann S
BACKGROUND
Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a debilitating, long-term illness that significantly impairs physical functioning. Despite its impact, the use of modern generic instruments to assess physical function in this population remains underexplored. This study aims to assess the psychometric properties of the Patient-Reported Outcome Measurement Information System® (PROMIS) Physical Function Short Form (PF-SF) 12a for use in adults with ME/CFS.
METHODS
This study included 334 participants (173 with ME/CFS and 161 healthy controls) who took part in a Cognitive and Exercise sub-study of the Multi-Site Clinical Assessment of ME/CFS study from six clinics across the US. Data was used to examine the ceiling/floor effects, internal consistency reliability, known-groups validity, and convergent validity of the PROMIS PF-SF.
RESULTS
The mean T-score of the PROMIS PF-SF was 40.5 for participants with ME/CFS, about one standard deviation below the national norm (T-score = 50). The PROMIS PF-SF showed no substantial floor/ceiling effects and high internal consistency (standardized Cronbach’s α = 0.88 and ω = 0.92). In addition, this instrument showed good known-groups validity with medium-to-large effect sizes (η2 = 0.08–0.35). A significant, monotonic increase of the physical function score was found across ME/CFS participant groups with low, medium, and high functional impairment as defined by four different measures. Participants with ME/CFS had significantly worse physical function scores than healthy controls (η2 = 0.70). The PROMIS PF-SF also demonstrated good convergent validity with high correlations (magnitude of r = 0.47–0.55) with other relevant measures.
CONCLUSIONS
The PROMIS PF-SF 12a demonstrated satisfactory reliability and validity for use in ME/CFS research and clinical practice.
Web | PDF | Health and Quality of Life Outcomes | Open Access