Interventional Removal of Travelling Microthrombi Using Targeted Magnetic Microbubble
Yongjian Li; Zujie Gao; Xiaobing Zheng; Yunfan Pan; Jinlong Xu; Yan Li; Haosheng Chen
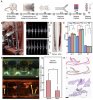
Microthrombus is one of the major causes of the sequelae of COVID-19 and leads to subsequent embolism and necrosis. Due to their small size and irregular movements, the early detection and efficient removal of microthrombi in vivo remain a great challenge.
In this work, an interventional method is developed to identify and remove the traveling microthrombi using targeted-magneticmicrobubbles (TMMBs) and an interventional magnetic catheter. The thrombus-targeted drugs are coated on the TMMBs and magnetic nanoparticles are shelled inside, which allow not only targeted adhesion onto the traveling microthrombi, but also the effective capture by the magnetic catheter in the vessel.
In the proof-of-concept experiments in the rat models, the concentration of microthrombus is reduced by more than 60% in 3 minutes, without damaging the organs. It is a promising method for treating microthrombus issues.
Link | PDF (Advanced Healthcare Materials)
Yongjian Li; Zujie Gao; Xiaobing Zheng; Yunfan Pan; Jinlong Xu; Yan Li; Haosheng Chen
Microthrombus is one of the major causes of the sequelae of COVID-19 and leads to subsequent embolism and necrosis. Due to their small size and irregular movements, the early detection and efficient removal of microthrombi in vivo remain a great challenge.
In this work, an interventional method is developed to identify and remove the traveling microthrombi using targeted-magneticmicrobubbles (TMMBs) and an interventional magnetic catheter. The thrombus-targeted drugs are coated on the TMMBs and magnetic nanoparticles are shelled inside, which allow not only targeted adhesion onto the traveling microthrombi, but also the effective capture by the magnetic catheter in the vessel.
In the proof-of-concept experiments in the rat models, the concentration of microthrombus is reduced by more than 60% in 3 minutes, without damaging the organs. It is a promising method for treating microthrombus issues.
Link | PDF (Advanced Healthcare Materials)