LarsSG
Senior Member (Voting Rights)
Key Points
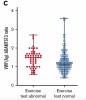
An elevated VWF(Ag):ADAMTS13 ratio (≥1.5) was raised in nearly one-third of the cohort and four times more likely in patients with impaired exercise capacity as evidenced by desaturation ≥3% and/or rise in lactate level more than 1 from baseline on 1-minute sit to stand test and/or 6-minute walk test (p<0.0001). 20% (56/276) had impaired exercise capacity, of which 55% (31/56) had a raised VWF(Ag):ADAMTS13 ratio ≥1.5 (p<0.0001). FVIII and VWF(Ag) were elevated in 26% and 18% respectively and support a hypercoagulable state in some patients with PCS. These findings suggest possible ongoing microvascular/endothelial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of PCS and highlight a potential role for antithrombotic therapy in the management of these patients.
Link with full text PDF
- VWF(Ag):ADAMTS13 ratio ≥1.5 was evident in 28% of PCS cohort
- 55% of patients with impaired exercise capacity had a raised VWF(Ag):ADAMTS13 ratio ≥1.5 (OR 4)
An elevated VWF(Ag):ADAMTS13 ratio (≥1.5) was raised in nearly one-third of the cohort and four times more likely in patients with impaired exercise capacity as evidenced by desaturation ≥3% and/or rise in lactate level more than 1 from baseline on 1-minute sit to stand test and/or 6-minute walk test (p<0.0001). 20% (56/276) had impaired exercise capacity, of which 55% (31/56) had a raised VWF(Ag):ADAMTS13 ratio ≥1.5 (p<0.0001). FVIII and VWF(Ag) were elevated in 26% and 18% respectively and support a hypercoagulable state in some patients with PCS. These findings suggest possible ongoing microvascular/endothelial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of PCS and highlight a potential role for antithrombotic therapy in the management of these patients.
Link with full text PDF