Genome-wide association studies of Long COVID and post-acute complications of SARS-CoV-2 in the UK Biobank Data
The genetic foundations of post-COVID-19 conditions remains unclear. We performed two genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in UK Biobank COVID-19 positive individuals to identify the genetic variants associated with Long COVID (LC) and post-acute cardiovascular complications of SARS-CoV-2 (PACS-CVD).
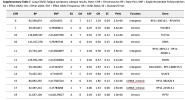
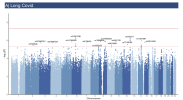
The LC cohort comprised 8,469 participants (68% cases). The PACS-CVD cohort included 105,175 individuals (2% cases). LC GWAS identified 15 independent signals at suggestive significance (p-value<5×10⁻⁶), with 73.3% validated.
The fully validated variant, rs12335232 (ADCY8), has been linked to memory decline, COVID-19 infection and severity. Other loci were near CHRNA7 (neuroinflammation, COVID-19 severity) and RNU7-126P (COVID-19 hospitalization). These findings consistently demonstrate shared biological pathways between acute infection and persistent symptoms. PACS-CVD GWAS identified 14 suggestive loci, mainly near genes linked to cardiovascular and metabolic functions (SAYSD1/KCNK5, FLT1) or COVID-19 severity (ROR2).
These results enhance the genetic understanding of Long COVID and PACS-CVD pathophysiology and highlight several potential therapeutic targets for both conditions.
Web | PDF | Preprint: Research Square | Open Access
Daniel Prieto-Alhambra; Marta Alcalde-Herraiz; Kim López-Güell; Shahed Iqbal; Jeffrey Wallin; Yunhao Liu; Jun Xie
The genetic foundations of post-COVID-19 conditions remains unclear. We performed two genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in UK Biobank COVID-19 positive individuals to identify the genetic variants associated with Long COVID (LC) and post-acute cardiovascular complications of SARS-CoV-2 (PACS-CVD).
The LC cohort comprised 8,469 participants (68% cases). The PACS-CVD cohort included 105,175 individuals (2% cases). LC GWAS identified 15 independent signals at suggestive significance (p-value<5×10⁻⁶), with 73.3% validated.
The fully validated variant, rs12335232 (ADCY8), has been linked to memory decline, COVID-19 infection and severity. Other loci were near CHRNA7 (neuroinflammation, COVID-19 severity) and RNU7-126P (COVID-19 hospitalization). These findings consistently demonstrate shared biological pathways between acute infection and persistent symptoms. PACS-CVD GWAS identified 14 suggestive loci, mainly near genes linked to cardiovascular and metabolic functions (SAYSD1/KCNK5, FLT1) or COVID-19 severity (ROR2).
These results enhance the genetic understanding of Long COVID and PACS-CVD pathophysiology and highlight several potential therapeutic targets for both conditions.
Web | PDF | Preprint: Research Square | Open Access