From Data to Insights: Machine Learning Empowers Prognostic Biomarker Prediction in Autism
Ecmel Mehmetbeyoglu; Abdulkerim Duman; Serpil Taheri; Yusuf Ozkul; Minoo Rassoulzadegan
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) poses significant challenges to society and science due to its impact on communication, social interaction, and repetitive behaviour patterns in affected children. The Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network continuously monitors ASD prevalence and characteristics. In 2020, ASD prevalence was estimated at one in 36 children, with higher rates than previous estimates.
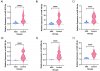
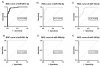
This study focuses on ongoing ASD research conducted by Erciyes University. Serum samples from 45 ASD patients and 21 unrelated control participants were analysed to assess the expression of 372 microRNAs (miRNAs). Six miRNAs (miR-19a-3p, miR-361-5p, miR-3613-3p, miR-150-5p, miR-126-3p, and miR-499a-5p) exhibited significant downregulation in all ASD patients compared to healthy controls. The current study endeavours to identify dependable diagnostic biomarkers for ASD, addressing the pressing need for non-invasive, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic tools, as current methods are subjective and time intensive.
A pivotal discovery in this study is the potential diagnostic value of miR-126-3p, offering the promise of earlier and more accurate ASD diagnoses, potentially leading to improved intervention outcomes. Leveraging machine learning, such as the K-nearest neighbours (KNN) model, presents a promising avenue for precise ASD diagnosis using miRNA biomarkers.
Link | PDF (Preprint: BioRxiv)
Ecmel Mehmetbeyoglu; Abdulkerim Duman; Serpil Taheri; Yusuf Ozkul; Minoo Rassoulzadegan
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) poses significant challenges to society and science due to its impact on communication, social interaction, and repetitive behaviour patterns in affected children. The Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network continuously monitors ASD prevalence and characteristics. In 2020, ASD prevalence was estimated at one in 36 children, with higher rates than previous estimates.
This study focuses on ongoing ASD research conducted by Erciyes University. Serum samples from 45 ASD patients and 21 unrelated control participants were analysed to assess the expression of 372 microRNAs (miRNAs). Six miRNAs (miR-19a-3p, miR-361-5p, miR-3613-3p, miR-150-5p, miR-126-3p, and miR-499a-5p) exhibited significant downregulation in all ASD patients compared to healthy controls. The current study endeavours to identify dependable diagnostic biomarkers for ASD, addressing the pressing need for non-invasive, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic tools, as current methods are subjective and time intensive.
A pivotal discovery in this study is the potential diagnostic value of miR-126-3p, offering the promise of earlier and more accurate ASD diagnoses, potentially leading to improved intervention outcomes. Leveraging machine learning, such as the K-nearest neighbours (KNN) model, presents a promising avenue for precise ASD diagnosis using miRNA biomarkers.
Link | PDF (Preprint: BioRxiv)