Chandelier
Senior Member (Voting Rights)
Effect of subcutaneous lidocaine–hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) on quality of life in patients with post-COVID condition: a 36-week observational interrupted time series study
The effects of currently applied treatments for post-COVID are limited.
This study assessed the effectiveness of subcutaneous lidocaine–hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) for the treatment of post-COVID.
Adults with physician-diagnosed post–COVID (n = 103) underwent a 4-week pre-treatment observation followed by 24–36 weeks of home-based subcutaneous lidocaine 5% with HP-β-CD, administered using a 3-phase protocol: 500 mg every other day (weeks 1–7), 500 mg daily (weeks 7–14), and up to 1000 mg/day (after week 14, in non-responders).
The primary outcome was health-related quality of life (Short Form-12 (SF-12), physical and mental component summary scores).
Secondary outcomes included symptom burden (daily app-based questionnaire) and adverse events.
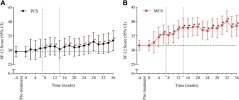
At week 24, the physical and mental component scores increased by 2·20 and 5·16 points, respectively; at week 36, by 4·13 and 7·00 points (all p < 0·0001).
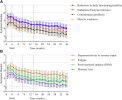
Twenty-seven of 30 symptoms improved significantly at week 24 of treatment compared to pre-treatment.
Mild adverse events occurred in 89% of participants, mostly injection–site reactions; no serious adverse events were reported.
This home-administered intervention offers a scalable and potentially disease-modifying approach for a disabling condition with no approved treatment to date.
Web | DOI | eClinicalMedicine
Oostwouder, Cees-Jan; Vos, Karin; Lutke Schipholt, Ivo J.; Merkus, Mathijs R.; Telders, Thomas; van Deursen, David F.A.; de Smit, Max B.; van Eijk, Marina D.; Bontkes, Hetty J.; Bouwman, Femke H.; Wüst, Rob C.I.; de Jong, Lara; van Hulst, Marinus; Twisk, Jos W.R.; van Kalken, Coenraad K.; Scholten-Peeters, Gwendolyne G.M.
Summary
Background
Post-COVID involves persistent, multisystem symptoms which are associated with inflammation, immune dysregulation, and autonomic dysfunction.The effects of currently applied treatments for post-COVID are limited.
This study assessed the effectiveness of subcutaneous lidocaine–hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) for the treatment of post-COVID.
Methods
This interrupted time series study was conducted at a Dutch outpatient clinic between August 2024 and April 2025.Adults with physician-diagnosed post–COVID (n = 103) underwent a 4-week pre-treatment observation followed by 24–36 weeks of home-based subcutaneous lidocaine 5% with HP-β-CD, administered using a 3-phase protocol: 500 mg every other day (weeks 1–7), 500 mg daily (weeks 7–14), and up to 1000 mg/day (after week 14, in non-responders).
The primary outcome was health-related quality of life (Short Form-12 (SF-12), physical and mental component summary scores).
Secondary outcomes included symptom burden (daily app-based questionnaire) and adverse events.
Findings
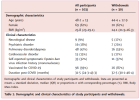
Among 103 participants (mean [SD] age 48·1 [13·0] years; 67% women; median [IQR] symptom duration 31·5 [24·3–43·3] months), 76% completed 24 weeks and 71% completed 36 weeks of treatment.At week 24, the physical and mental component scores increased by 2·20 and 5·16 points, respectively; at week 36, by 4·13 and 7·00 points (all p < 0·0001).
Twenty-seven of 30 symptoms improved significantly at week 24 of treatment compared to pre-treatment.
Mild adverse events occurred in 89% of participants, mostly injection–site reactions; no serious adverse events were reported.
Interpretation
Subcutaneous lidocaine–HP-β-CD was associated with significantly improved quality of life and symptom burden in patients with post–COVID.This home-administered intervention offers a scalable and potentially disease-modifying approach for a disabling condition with no approved treatment to date.
Funding
Excellent Care Clinics funded the treatment provided in this study.Web | DOI | eClinicalMedicine