hotblack
Senior Member (Voting Rights)
An emerging role for calcium signalling in innate and autoimmunity via the cGAS-STING axis
Mathavarajah, Sabateeshan; Salsman, Jayme; Dellaire, Graham
Abstract
Type I interferons are effector cytokines essential for the regulation of the innate immunity. A key effector of the type I interferon response that is dysregulated in autoimmunity and cancer is the cGAS-STING signalling axis.
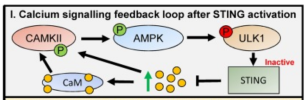
Recent work suggests that calcium and associated signalling proteins can regulate both cGAS-STING and autoimmunity. How calcium regulates STING activation is complex and involves both stimulatory and inhibitory mechanisms.
One of these is calmodulin-mediated signalling that is necessary for STING activation. The alterations in calcium flux that occur during STING activation can also regulate autophagy, which in turn plays a role in innate immunity through the clearance of intracellular pathogens. Also connected to calcium signalling pathways is the cGAS inhibitor TREX1, a cytoplasmic exonuclease linked to several autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
In this review, we summarize these and other findings that indicate a regulatory role for calcium signalling in innate and autoimmunity through the cGAS-STING pathway.
Web | DOI | Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews
Mathavarajah, Sabateeshan; Salsman, Jayme; Dellaire, Graham
Abstract
Type I interferons are effector cytokines essential for the regulation of the innate immunity. A key effector of the type I interferon response that is dysregulated in autoimmunity and cancer is the cGAS-STING signalling axis.
Recent work suggests that calcium and associated signalling proteins can regulate both cGAS-STING and autoimmunity. How calcium regulates STING activation is complex and involves both stimulatory and inhibitory mechanisms.
One of these is calmodulin-mediated signalling that is necessary for STING activation. The alterations in calcium flux that occur during STING activation can also regulate autophagy, which in turn plays a role in innate immunity through the clearance of intracellular pathogens. Also connected to calcium signalling pathways is the cGAS inhibitor TREX1, a cytoplasmic exonuclease linked to several autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
In this review, we summarize these and other findings that indicate a regulatory role for calcium signalling in innate and autoimmunity through the cGAS-STING pathway.
Web | DOI | Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews