Vitamins K2 and D3 Improve Long COVID, Fungal Translocation, and Inflammation: Randomized Controlled Trial
Ornina Atieh, Joviane Daher, Jared C Durieux, Marc Abboud, Danielle Labbato, Jhony Baissary, Ziad Koberssy, Kate Ailstock, Morgan Cummings, Nicholas T Funderburg, Grace A McComsey
Background
Long COVID (LC) is characterized by persistent symptoms at least 3 months after a SARS-COV-2 infection. LC has been associated with fungal translocation, gut dysfunction, and enhanced systemic inflammation. Currently, there is no approved treatment for this condition. The anti-inflammatory effect of vitamins K2 and D3 was shown to help attenuate the course of acute COVID-19 infection.
Objective and hypothesis
This trial aims to investigate the effects of vitamins K2/D3 on LC symptoms, as well as gut and inflammatory markers, in people with established long COVID. Our hypothesis is that by attenuating systemic inflammation, vitamins K2/D3 will improve long COVID symptoms.
Methods
This single-site randomized controlled study enrolled adults experiencing ≥2 moderate LC symptoms at least 3 months after a COVID-19 infection. The RECOVER Long COVID Research Index and number and type of LC symptoms were considered. Participants were randomized 2:1 to daily 240 µg K2 (pure MK-7 form) and 2000 UI vitamin D3 or standard of care (SOC) for 24 weeks. The endpoints were changes in symptomatology and in select inflammatory, metabolic, and gut biomarkers at 24 weeks.
Results
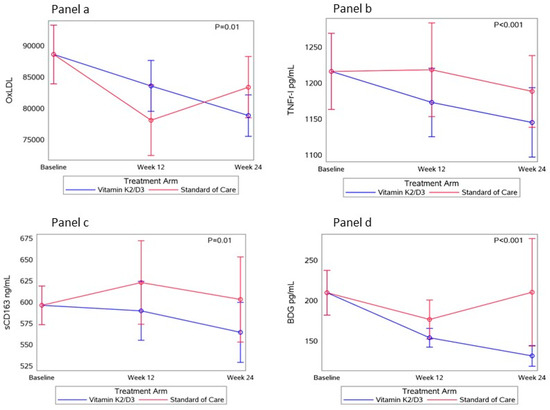
We enrolled 151 participants (n = 98 received vit K2/D3 and 53 received SOC). The median age was 46 years; 71% were female and 29% were non-white. Baseline demographics were balanced between groups. At 24 weeks, the active treatment group only had a sharp increase in 25(OH) D, indicating good treatment adherence. In the vitamin K2/D3 arm, there was a 7.1% decrease in the proportion who had an LC Index ≥12 (vs. a 7.2% increase in the SOC group; p = 0.01). The average number of LC symptoms remained stable in the vitamin K2/D3 arm but increased in the SOC arm (p = 0.03). Additionally, reductions in oxidized LDL, inflammatory markers sTNF-RI and sCD163, and fungal translocation marker (1,3)-β-d-glucan were observed in the vitamin K2/D3 arm compared to the SOC arm (p < 0.01) over 24 weeks.
Conclusions
Vitamins K2/D3 improved the RECOVER Long COVID Index, the number of LC symptoms, and several gut and inflammatory markers. Vitamins K2/D3 provide a promising safe intervention for people suffering from long COVID.
Link | PDF (Nutrients) [Open Access]
Ornina Atieh, Joviane Daher, Jared C Durieux, Marc Abboud, Danielle Labbato, Jhony Baissary, Ziad Koberssy, Kate Ailstock, Morgan Cummings, Nicholas T Funderburg, Grace A McComsey
Background
Long COVID (LC) is characterized by persistent symptoms at least 3 months after a SARS-COV-2 infection. LC has been associated with fungal translocation, gut dysfunction, and enhanced systemic inflammation. Currently, there is no approved treatment for this condition. The anti-inflammatory effect of vitamins K2 and D3 was shown to help attenuate the course of acute COVID-19 infection.
Objective and hypothesis
This trial aims to investigate the effects of vitamins K2/D3 on LC symptoms, as well as gut and inflammatory markers, in people with established long COVID. Our hypothesis is that by attenuating systemic inflammation, vitamins K2/D3 will improve long COVID symptoms.
Methods
This single-site randomized controlled study enrolled adults experiencing ≥2 moderate LC symptoms at least 3 months after a COVID-19 infection. The RECOVER Long COVID Research Index and number and type of LC symptoms were considered. Participants were randomized 2:1 to daily 240 µg K2 (pure MK-7 form) and 2000 UI vitamin D3 or standard of care (SOC) for 24 weeks. The endpoints were changes in symptomatology and in select inflammatory, metabolic, and gut biomarkers at 24 weeks.
Results
We enrolled 151 participants (n = 98 received vit K2/D3 and 53 received SOC). The median age was 46 years; 71% were female and 29% were non-white. Baseline demographics were balanced between groups. At 24 weeks, the active treatment group only had a sharp increase in 25(OH) D, indicating good treatment adherence. In the vitamin K2/D3 arm, there was a 7.1% decrease in the proportion who had an LC Index ≥12 (vs. a 7.2% increase in the SOC group; p = 0.01). The average number of LC symptoms remained stable in the vitamin K2/D3 arm but increased in the SOC arm (p = 0.03). Additionally, reductions in oxidized LDL, inflammatory markers sTNF-RI and sCD163, and fungal translocation marker (1,3)-β-d-glucan were observed in the vitamin K2/D3 arm compared to the SOC arm (p < 0.01) over 24 weeks.
Conclusions
Vitamins K2/D3 improved the RECOVER Long COVID Index, the number of LC symptoms, and several gut and inflammatory markers. Vitamins K2/D3 provide a promising safe intervention for people suffering from long COVID.
Link | PDF (Nutrients) [Open Access]