Vagus nerve inflammation contributes to dysautonomia in COVID-19
Woo, Marcel S.; Shafiq, Mohsin; Fitzek, Antonia; Dottermusch, Matthias; Altmeppen, Hermann; Mohammadi, Behnam; Mayer, Christina; Bal, Lukas C.; Raich, Lukas; Matschke, Jakob; Krasemann, Susanne; Pfefferle, Susanne; Brehm, Thomas Theo; Lütgehetmann, Marc; Schädler, Julia; Addo, Marylyn M.; Schulze zur Wiesch, Julian; Ondruschka, Benjamin; Friese, Manuel A.; Glatzel, Markus
Dysautonomia has substantially impacted acute COVID-19 severity as well as symptom burden after recovery from COVID-19 (long COVID), yet the underlying causes remain unknown. Here, we hypothesized that vagus nerves are affected in COVID-19 which might contribute to autonomic dysfunction.
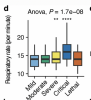
We performed a histopathological characterization of postmortem vagus nerves from COVID-19 patients and controls, and detected SARS-CoV-2 RNA together with inflammatory cell infiltration composed primarily of monocytes. Furthermore, we performed RNA sequencing which revealed a strong inflammatory response of neurons, endothelial cells, and Schwann cells which correlated with SARS-CoV-2 RNA load. Lastly, we screened a clinical cohort of 323 patients to detect a clinical phenotype of vagus nerve affection and found a decreased respiratory rate in non-survivors of critical COVID-19.
Our data suggest that SARS-CoV-2 induces vagus nerve inflammation followed by autonomic dysfunction which contributes to critical disease courses and might contribute to dysautonomia observed in long COVID.
Link | PDF (Acta Neuropathologica)
Woo, Marcel S.; Shafiq, Mohsin; Fitzek, Antonia; Dottermusch, Matthias; Altmeppen, Hermann; Mohammadi, Behnam; Mayer, Christina; Bal, Lukas C.; Raich, Lukas; Matschke, Jakob; Krasemann, Susanne; Pfefferle, Susanne; Brehm, Thomas Theo; Lütgehetmann, Marc; Schädler, Julia; Addo, Marylyn M.; Schulze zur Wiesch, Julian; Ondruschka, Benjamin; Friese, Manuel A.; Glatzel, Markus
Dysautonomia has substantially impacted acute COVID-19 severity as well as symptom burden after recovery from COVID-19 (long COVID), yet the underlying causes remain unknown. Here, we hypothesized that vagus nerves are affected in COVID-19 which might contribute to autonomic dysfunction.
We performed a histopathological characterization of postmortem vagus nerves from COVID-19 patients and controls, and detected SARS-CoV-2 RNA together with inflammatory cell infiltration composed primarily of monocytes. Furthermore, we performed RNA sequencing which revealed a strong inflammatory response of neurons, endothelial cells, and Schwann cells which correlated with SARS-CoV-2 RNA load. Lastly, we screened a clinical cohort of 323 patients to detect a clinical phenotype of vagus nerve affection and found a decreased respiratory rate in non-survivors of critical COVID-19.
Our data suggest that SARS-CoV-2 induces vagus nerve inflammation followed by autonomic dysfunction which contributes to critical disease courses and might contribute to dysautonomia observed in long COVID.
Link | PDF (Acta Neuropathologica)