SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Amyloid Fibrils Impair Fibrin Formation and Fibrinolysis
Henrik Westman; Per Hammarström; Sofie Nyström
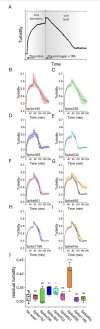
Long COVID, or postacute sequelae of COVID-19 from SARS-CoV-2 infection, is a persistent debilitating disease affecting multiple systems and organs. Long COVID pathophysiology is a complex and not fully established process. One prevailing theory is that the formation of fibrin amyloid microclots (fibrinaloids), due to SARS-CoV-2 infection, can induce persistent inflammation and capillary blockage. An association between the amyloidogenic Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 and impaired fibrinolysis was made when it was observed that fibrin clots formed in the presence of a mixture of amyloid fibrils from the spike protein mediated resistance to plasmin lysis.
Here, we use purified components from the coagulation cascade to investigate the molecular processes of impaired fibrinolysis using seven amyloidogenic SARS-COV-2 Spike peptides. Five of seven Spike amyloid fibrils appeared not to substantially interfere with the fibrinogen–fibrin–fibrinolysis process in vitro, while two spike fibrils were active in different ways. Spike601 amyloid fibrils (sequence 601–620) impaired thrombin-mediated fibrin formation by binding and sequestering fibrinogen but did not affect fibrinolysis. On the contrary, fibrin clots formed in the presence of Spike685 amyloid fibrils (sequence 685–701) exhibited a marked resistance to plasmin-mediated fibrinolysis.
We conclude that Spike685 amyloid fibrils can induce dense fibrin clot networks as well as incorporate fibrin into aggregated structures that resist fibrinolysis. Our study proposes a molecular mechanism for how the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 could contribute to the formation of fibrinolysis-resistant microclots observed in long COVID.
Web | DOI | PDF | Biochemistry | Open Access
Henrik Westman; Per Hammarström; Sofie Nyström
Long COVID, or postacute sequelae of COVID-19 from SARS-CoV-2 infection, is a persistent debilitating disease affecting multiple systems and organs. Long COVID pathophysiology is a complex and not fully established process. One prevailing theory is that the formation of fibrin amyloid microclots (fibrinaloids), due to SARS-CoV-2 infection, can induce persistent inflammation and capillary blockage. An association between the amyloidogenic Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 and impaired fibrinolysis was made when it was observed that fibrin clots formed in the presence of a mixture of amyloid fibrils from the spike protein mediated resistance to plasmin lysis.
Here, we use purified components from the coagulation cascade to investigate the molecular processes of impaired fibrinolysis using seven amyloidogenic SARS-COV-2 Spike peptides. Five of seven Spike amyloid fibrils appeared not to substantially interfere with the fibrinogen–fibrin–fibrinolysis process in vitro, while two spike fibrils were active in different ways. Spike601 amyloid fibrils (sequence 601–620) impaired thrombin-mediated fibrin formation by binding and sequestering fibrinogen but did not affect fibrinolysis. On the contrary, fibrin clots formed in the presence of Spike685 amyloid fibrils (sequence 685–701) exhibited a marked resistance to plasmin-mediated fibrinolysis.
We conclude that Spike685 amyloid fibrils can induce dense fibrin clot networks as well as incorporate fibrin into aggregated structures that resist fibrinolysis. Our study proposes a molecular mechanism for how the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 could contribute to the formation of fibrinolysis-resistant microclots observed in long COVID.
Web | DOI | PDF | Biochemistry | Open Access