Sly Saint
Senior Member (Voting Rights)
Abstract
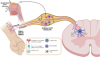
There is a clear clinical overlap between fibromyalgia, myalgic encephalomyelitis, and post-COVID 19 condition. Chronic fatigue, cognitive impairment, and widespread pain characterize these 3 syndromes. A steady line of investigation posits fibromyalgia as stress-evoked sympathetically maintained neuropathic pain syndrome and places dorsal root ganglia dysregulation with the ensuing small fiber neuropathy at the epicenter of fibromyalgia pathogenesis. This article discusses emerging evidence suggesting that similar mechanism may operate in post-COVID 19 condition.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10067-023-06743-0
paywalled
There is a clear clinical overlap between fibromyalgia, myalgic encephalomyelitis, and post-COVID 19 condition. Chronic fatigue, cognitive impairment, and widespread pain characterize these 3 syndromes. A steady line of investigation posits fibromyalgia as stress-evoked sympathetically maintained neuropathic pain syndrome and places dorsal root ganglia dysregulation with the ensuing small fiber neuropathy at the epicenter of fibromyalgia pathogenesis. This article discusses emerging evidence suggesting that similar mechanism may operate in post-COVID 19 condition.

https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10067-023-06743-0
paywalled
