Andy
Senior Member (Voting rights)
Full title: Effects of l-Arginine Plus Vitamin C Supplementation on Physical Performance, Endothelial Function, and Persistent Fatigue in Adults with Long COVID: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Long COVID, a condition characterized by symptom and/or sign persistence following an acute COVID-19 episode, is associated with reduced physical performance and endothelial dysfunction. Supplementation of l-arginine may improve endothelial and muscle function by stimulating nitric oxide synthesis.
A single-blind randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted in adults aged between 20 and 60 years with persistent fatigue attending a post-acute COVID-19 outpatient clinic. Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive twice-daily orally either a combination of 1.66 g l-arginine plus 500 mg liposomal vitamin C or a placebo for 28 days. The primary outcome was the distance walked on the 6 min walk test. Secondary outcomes were handgrip strength, flow-mediated dilation, and fatigue persistence. Fifty participants were randomized to receive either l-arginine plus vitamin C or a placebo. Forty-six participants (median (interquartile range) age 51 (14), 30 [65%] women), 23 per group, received the intervention to which they were allocated and completed the study.
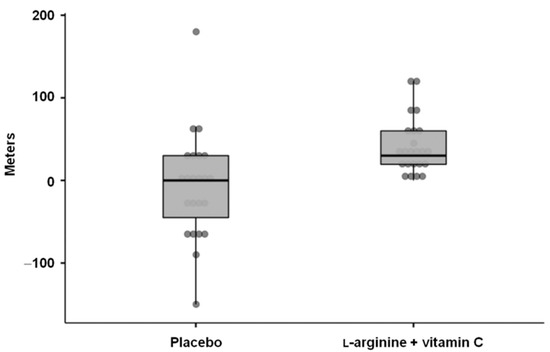
At 28 days, l-arginine plus vitamin C increased the 6 min walk distance (+30 (40.5) m; placebo: +0 (75) m, p = 0.001) and induced a greater improvement in handgrip strength (+3.4 (7.5) kg) compared with the placebo (+1 (6.6) kg, p = 0.03). The flow-mediated dilation was greater in the active group than in the placebo (14.3% (7.3) vs. 9.4% (5.8), p = 0.03). At 28 days, fatigue was reported by two participants in the active group (8.7%) and 21 in the placebo group (80.1%; p < 0.0001). l-arginine plus vitamin C supplementation improved walking performance, muscle strength, endothelial function, and fatigue in adults with long COVID.
This supplement may, therefore, be considered to restore physical performance and relieve persistent symptoms in this patient population.
Open access, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/23/4984
Abstract
Long COVID, a condition characterized by symptom and/or sign persistence following an acute COVID-19 episode, is associated with reduced physical performance and endothelial dysfunction. Supplementation of l-arginine may improve endothelial and muscle function by stimulating nitric oxide synthesis.
A single-blind randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted in adults aged between 20 and 60 years with persistent fatigue attending a post-acute COVID-19 outpatient clinic. Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive twice-daily orally either a combination of 1.66 g l-arginine plus 500 mg liposomal vitamin C or a placebo for 28 days. The primary outcome was the distance walked on the 6 min walk test. Secondary outcomes were handgrip strength, flow-mediated dilation, and fatigue persistence. Fifty participants were randomized to receive either l-arginine plus vitamin C or a placebo. Forty-six participants (median (interquartile range) age 51 (14), 30 [65%] women), 23 per group, received the intervention to which they were allocated and completed the study.
At 28 days, l-arginine plus vitamin C increased the 6 min walk distance (+30 (40.5) m; placebo: +0 (75) m, p = 0.001) and induced a greater improvement in handgrip strength (+3.4 (7.5) kg) compared with the placebo (+1 (6.6) kg, p = 0.03). The flow-mediated dilation was greater in the active group than in the placebo (14.3% (7.3) vs. 9.4% (5.8), p = 0.03). At 28 days, fatigue was reported by two participants in the active group (8.7%) and 21 in the placebo group (80.1%; p < 0.0001). l-arginine plus vitamin C supplementation improved walking performance, muscle strength, endothelial function, and fatigue in adults with long COVID.
This supplement may, therefore, be considered to restore physical performance and relieve persistent symptoms in this patient population.
Open access, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/23/4984