Simon M
Senior Member (Voting Rights)
Shortened version– read the full blog here.
Scientists, people with ME/CFS, and their charities came together to create DecodeME, the world's biggest ME/CFS study – and its results are striking. 18,000 people with ME/CFS gave their DNA, enabling DecodeME to reveal eight genetic signals for the illness. These signals indicate that immune and neurological processes play a significant role in ME/CFS.
Why a DNA study?
We know little about the biology of ME/CFS, which makes it very hard to develop effective treatments. Usually, we can’t tell if the biological differences studies find between those with ME and those without are a cause of the disease, or an effect. DNA is different because diseases don’t change our DNA.
DNA carries the instructions for how to make and run a human body. It’s effectively a very long string of four different chemicals, named A, T, C and G for short. Some of these letters make up our roughly 20,000 genes, and each gene carries the recipe for making a particular kind of protein. Proteins are our bodies’ ‘doing’ molecules, such as digestive enzymes, antibodies and components of muscle fibres.
As most proteins do something very specific, if we can pinpoint which genes are different in people with ME/CFS, we also pinpoint the protein involved – and that points to the biology.
How DecodeME looked for DNA differences
DecodeME was a genome-wide association study (GWAS). These studies don’t look for DNA differences in each of the three billion DNA letters that humans have, because that’s very expensive. Instead, they look only in those places where people often have different letters from each other (each different letter at a particular location is a ‘variant’). DecodeME looked at nearly nine million of the DNA letters, but that is still only three in every thousand letters.
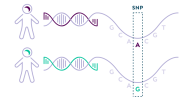
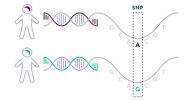 Caption: Illustration of a DNA variant where one person has DNA with the letter A, while another has the letter G at the same position.
Caption: Illustration of a DNA variant where one person has DNA with the letter A, while another has the letter G at the same position.
DecodeME’s findings
DecodeME looked at the DNA of 15,579 people with an ME/CFS diagnosis who met the study’s tight research criteria and compared it with the DNA of nearly 260,000 controls without ME/CFS…
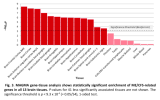
The analysis revealed eight genetic ‘signals’ for ME/CFS from the nine million variants studied. And these signals will help to reveal the biology of the disease.
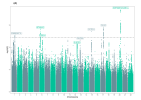
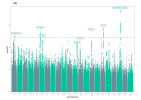
You can see these signals as the peaks (‘skyscrapers’) that stick up above the dotted line in the ‘Manhattan plot’ below. They show where there are groups of variants that are significantly different in people with ME/CFS compared to healthy people. These peaks, or signals, are each flagged with the name of the gene that could explain them.
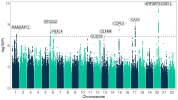
Image: [Manhattan plot for the main DecodeME GWAS showing 6 of the eight genetic signals. Two that were just below the threshold were above it in two other GWAS using DecodeME participants – see blog]
The genetic signals are like crosses on a treasure map, pointing to hidden biology.
GWAS are an affordable way to scan the human genome but are harder to interpret because they only look directly at a few DNA letters in every million. This means that although there are eight genetic signals of closely-grouped variants significantly associated with ME/CFS, the DNA defined by the signal will contain many unseen variants. These unseen variants are more likely to be a cause of ME/CFS because there are far more of them.
So each genetic signal is like an ‘X’ on a treasure map indicating roughly where the researchers should dig for treasure. The next step is to find that treasure – the specific genes that are causing ME/CFS.
DecodeME identifies top genes
DecodeME has started searching for the treasure, and has identified likely genes using several methods. These methods looked at genes within the genetic signals – the peaks on the Manhattan plot.
… see the blog for more details, but the most likely genes mainly relate to problems tackling an infection, plus neurological processes including pain.
…So, DecodeME showed that immunological and neurological processes are likely to play a part in ME/CFS. They also found a link to chronic pain,
DecodeME also looked at genetic signals associated with depression and anxiety that were near the genetic signals found for ME/CFS
So, DecodeME showed that immunological and neurological processes are likely to play a part in ME/CFS. They also found a link to chronic pain, but not to anxiety or depression.
Researchers could flood in to transform the field
The real story here is that DecodeME has generated a host of new biological clues.
Sonya Chowdhury, chair of DecodeME’s management group and CEO of Action for ME, said, ‘These results are groundbreaking. With DecodeME, we have gone from knowing next to nothing about the causes of ME/CFS, to giving researchers clear targets.’
She added, ‘We hope this attracts researchers, drug developers, and fair funding to ME/CFS – and speeds up the discovery of treatments.’
Read the full blog
Scientists, people with ME/CFS, and their charities came together to create DecodeME, the world's biggest ME/CFS study – and its results are striking. 18,000 people with ME/CFS gave their DNA, enabling DecodeME to reveal eight genetic signals for the illness. These signals indicate that immune and neurological processes play a significant role in ME/CFS.
Why a DNA study?
We know little about the biology of ME/CFS, which makes it very hard to develop effective treatments. Usually, we can’t tell if the biological differences studies find between those with ME and those without are a cause of the disease, or an effect. DNA is different because diseases don’t change our DNA.
DNA carries the instructions for how to make and run a human body. It’s effectively a very long string of four different chemicals, named A, T, C and G for short. Some of these letters make up our roughly 20,000 genes, and each gene carries the recipe for making a particular kind of protein. Proteins are our bodies’ ‘doing’ molecules, such as digestive enzymes, antibodies and components of muscle fibres.

As most proteins do something very specific, if we can pinpoint which genes are different in people with ME/CFS, we also pinpoint the protein involved – and that points to the biology.
How DecodeME looked for DNA differences
DecodeME was a genome-wide association study (GWAS). These studies don’t look for DNA differences in each of the three billion DNA letters that humans have, because that’s very expensive. Instead, they look only in those places where people often have different letters from each other (each different letter at a particular location is a ‘variant’). DecodeME looked at nearly nine million of the DNA letters, but that is still only three in every thousand letters.
 Caption: Illustration of a DNA variant where one person has DNA with the letter A, while another has the letter G at the same position.
Caption: Illustration of a DNA variant where one person has DNA with the letter A, while another has the letter G at the same position.DecodeME’s findings
DecodeME looked at the DNA of 15,579 people with an ME/CFS diagnosis who met the study’s tight research criteria and compared it with the DNA of nearly 260,000 controls without ME/CFS…
The analysis revealed eight genetic ‘signals’ for ME/CFS from the nine million variants studied. And these signals will help to reveal the biology of the disease.
You can see these signals as the peaks (‘skyscrapers’) that stick up above the dotted line in the ‘Manhattan plot’ below. They show where there are groups of variants that are significantly different in people with ME/CFS compared to healthy people. These peaks, or signals, are each flagged with the name of the gene that could explain them.

Image: [Manhattan plot for the main DecodeME GWAS showing 6 of the eight genetic signals. Two that were just below the threshold were above it in two other GWAS using DecodeME participants – see blog]
The genetic signals are like crosses on a treasure map, pointing to hidden biology.
GWAS are an affordable way to scan the human genome but are harder to interpret because they only look directly at a few DNA letters in every million. This means that although there are eight genetic signals of closely-grouped variants significantly associated with ME/CFS, the DNA defined by the signal will contain many unseen variants. These unseen variants are more likely to be a cause of ME/CFS because there are far more of them.
So each genetic signal is like an ‘X’ on a treasure map indicating roughly where the researchers should dig for treasure. The next step is to find that treasure – the specific genes that are causing ME/CFS.
DecodeME identifies top genes
DecodeME has started searching for the treasure, and has identified likely genes using several methods. These methods looked at genes within the genetic signals – the peaks on the Manhattan plot.
… see the blog for more details, but the most likely genes mainly relate to problems tackling an infection, plus neurological processes including pain.
…So, DecodeME showed that immunological and neurological processes are likely to play a part in ME/CFS. They also found a link to chronic pain,
DecodeME also looked at genetic signals associated with depression and anxiety that were near the genetic signals found for ME/CFS
So, DecodeME showed that immunological and neurological processes are likely to play a part in ME/CFS. They also found a link to chronic pain, but not to anxiety or depression.
Researchers could flood in to transform the field
The real story here is that DecodeME has generated a host of new biological clues.
Sonya Chowdhury, chair of DecodeME’s management group and CEO of Action for ME, said, ‘These results are groundbreaking. With DecodeME, we have gone from knowing next to nothing about the causes of ME/CFS, to giving researchers clear targets.’
She added, ‘We hope this attracts researchers, drug developers, and fair funding to ME/CFS – and speeds up the discovery of treatments.’
Read the full blog
Attachments
Last edited: